

English
All databases support indexes, and index files provide a quick way to query records by taking up additional disk space. When querying, query the index file first, and then query the real data according to the instructions of the index file, which has obvious performance advantages when the amount of data is large.
Indexes serve two purposes:
If your query operation includes filtering conditions (including equivalence testing and range filtering) or sorting, or requires uniqueness, consider adding indexes to the relevant fields of the collection. Generally speaking, it is necessary to add indexes where, match, orderBy, sort for the field used in the following methods/properties, and also include the startWith attribute of getTree and getTreePath in clientDB.
If the related field is not set as an index, when the number of records in the data table increases, the query will slow down or even get an error over time. This is especially important to note. Some developers have already experienced online glitches. There is no index during development, because the amount of data is small and there is no performance problem. After going online, the amount of data becomes larger and larger, and the query becomes slower and slower until it times out, causing online accidents.
Notice:
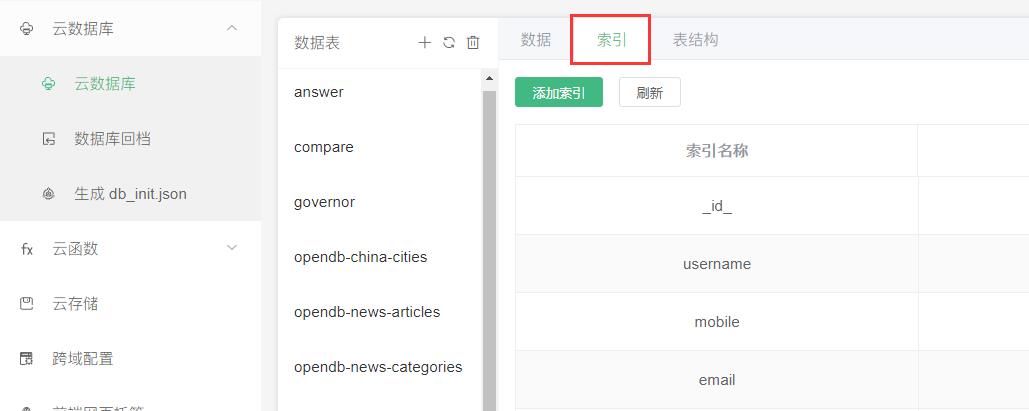
In db_init.json, you can set an index for a specific collection by writing the following method (recommended to use it when the service space is initialized)
{
"opendb-news-article": {
"data": [],
"index":[{
"IndexName": "user_article_", // 索引名称
"MgoKeySchema": { // 索引规则
"MgoIndexKeys": [{
"Name": "user_id", // 索引字段
"Direction": "1" // 索引方向,1:ASC-升序,-1:DESC-降序,2dsphere:地理位置
},{
"Name": "article_id", // 索引字段
"Direction": "1" // 索引方向,1:ASC-升序,-1:DESC-降序,2dsphere:地理位置
}],
"MgoIsUnique": false // 索引是否唯一
}
}]
}
}
You can create a single-field index for the field corresponding to the query condition. If the field is a nested field, you can use "dot notation". For example, when indexing the color field in a record of the following format, it can be represented by style.color.
{
"_id": "",
"style": {
"color": ""
}
}
When setting a single-field index, you can arbitrarily specify that the index is sorted in ascending or descending order, and the database can always perform the correct sorting in the sorting query of the index field.
A composite index is an index that contains multiple fields. When the fields used by the query conditions are included in all the fields or prefix fields defined by the index, the index will be hit and the query performance will be optimized.
The index prefix is the first 1 or more fields defined in the fields of the combined index, for example, the three fields name, age, score in the collection students are defined in order combined index, then the prefix of the index contains
- name
- name, age
The combination of query fields that can hit the index includes
- name
- name, age
- name, age, score
{
"_id": "1",
"name": "luke",
"age": 26,
"score": 80
}
Combined index The order of fields determines the combined index effect
For example, defining a composite index as name, age and age, name are different. When the combined index is name, age, its index prefix is name, the query on the field name can hit the name, age index, and the field *age * The query cannot hit the index, because age does not belong to the prefix of name, age (conversely, the field age can hit the age, name index).
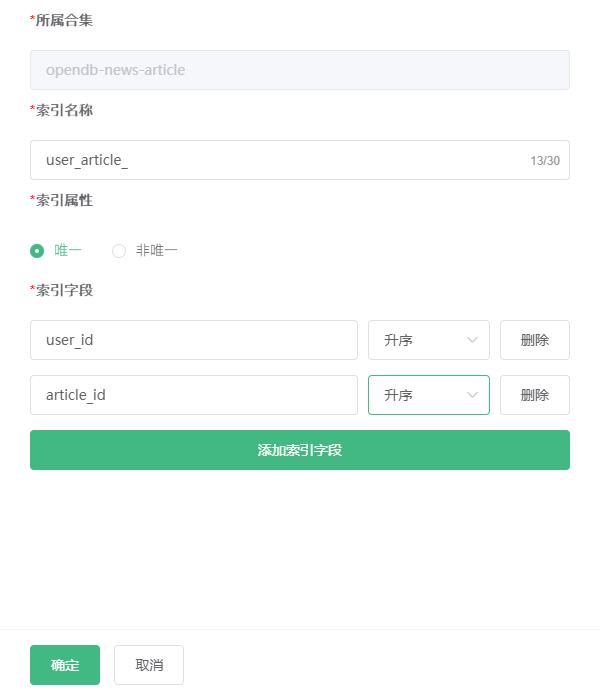
ApsaraDB for Cloud Database currently supports the establishment of a geographic location index for plane geometry. When using the geographic location query function, a geographic location index must be established for the fields of the geographic location data.
For example, create a geographic index for a collection with a geographic field point:
{
"_id": "",
"point": new db.Geo.Point(50, 50)
}
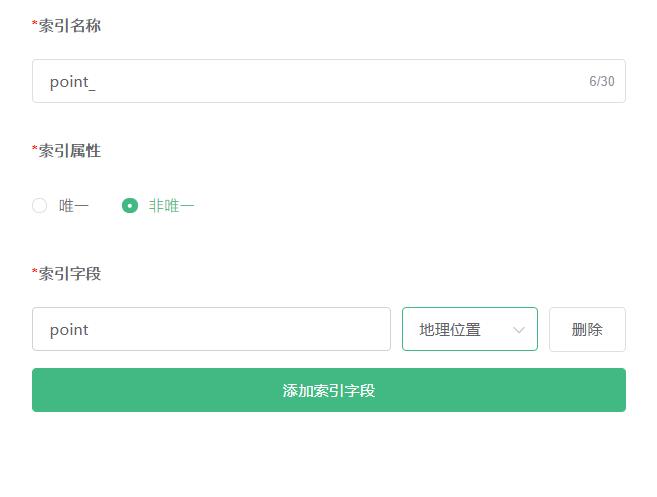
The ttl index is used to set the data expiration time and delete the data after it expires. Only supported by Alibaba Cloud
The configuration is as follows:
Notice
When creating an index, select UNIQUE for the index property to add a uniqueness restriction. This restriction requires that the value corresponding to the index field in the collection cannot be repeated.
For example, if the index field foo is established in a collection, and the attribute is "unique", then in this collection, it is required that no documents with the same field foo exist.
Notice
If a field does not exist in the record, its value defaults to null for the index field. If the index has a uniqueness restriction, it is not allowed to have two or more records where the field is empty/doesn't exist.
In response to the above problems, Alibaba Cloud supports setting the index to sparse index, while Tencent Cloud does not support sparse index.
Only supported by Alibaba Cloud
Sparse indexes are suitable for scenarios where a field needs to be unique, but the field may be empty. Taking the user table as an example, users may register by email or by mobile phone number, so it is necessary to ensure that the mailbox and mobile phone number are unique and allowed to be empty. At this time, the indexes of mailboxes and mobile phone numbers can be set as sparse indexes respectively. to handle this scenario. Note that uni-id supports multi-application user isolation (the same mobile phone number, email, etc. can be registered in different applications), and mobile phone numbers, emails, etc. cannot be set to unique indexes
Configure the index as a sparse index
That is, do not index large pieces of text (such as news content)
Each English letter (case-insensitive) occupies a space of one byte, and each Chinese character occupies a space of two bytes.
Regular queries cannot use indexes to improve performance.